
“Performance of MAR (v3.11) in simulating the drifting-snow climate and surface mass balance of Adélie Land, East Antarctica” was published in Geoscientific Model Development.
Here are the main findings:
- Drifting snow is now part of the physics embedded in the regional climate model MAR (v3.11).
- Drifting snow creates layers of suspended snow remobilised from the surface by the wind up to several hundreds of meters in thickness, similarly to thin low-level clouds.
- It has important implications for the Antarctic climate and snow accumulation on the IceSheet and is yet ignored in most climate models.
- This process is frequent in Adelie Land, one of the windiest place of East Antarctica.
- Our new version of the regional climate model MAR reproduces very well observed drifting snow and the resulting snow accumulation in Adelie Land.
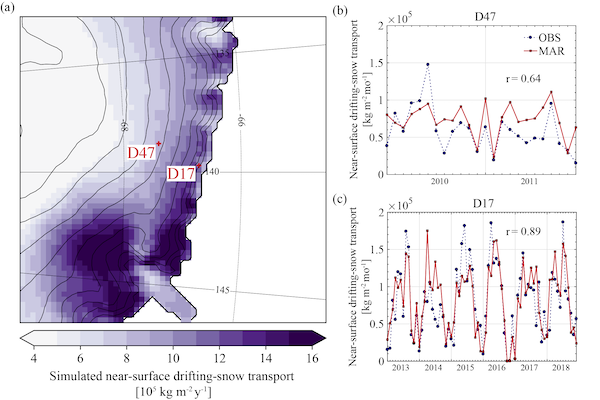
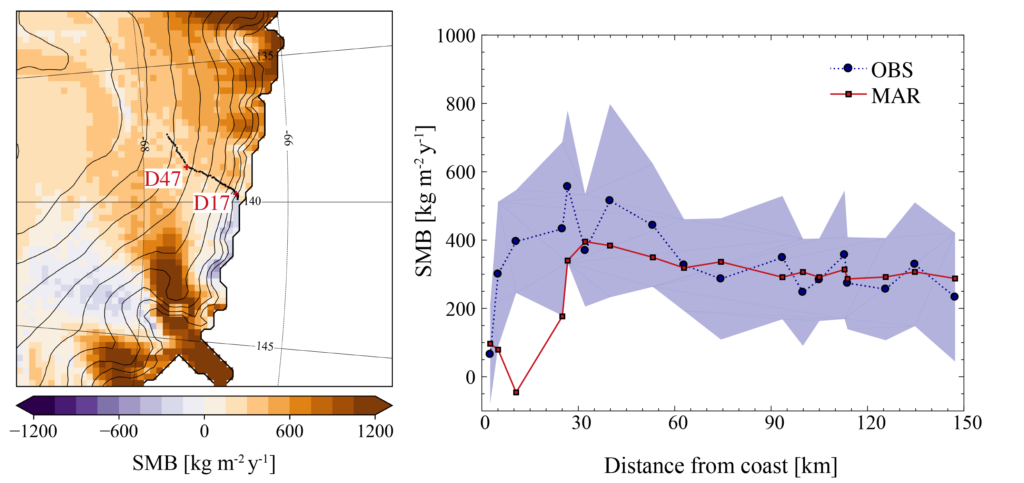
- Next continent-wide investigations of snow accumulation in Antarctica with MAR will include this process. A lot more to come, stay tuned!
Link to the paper: https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-14-3487-2021

Leave a Reply