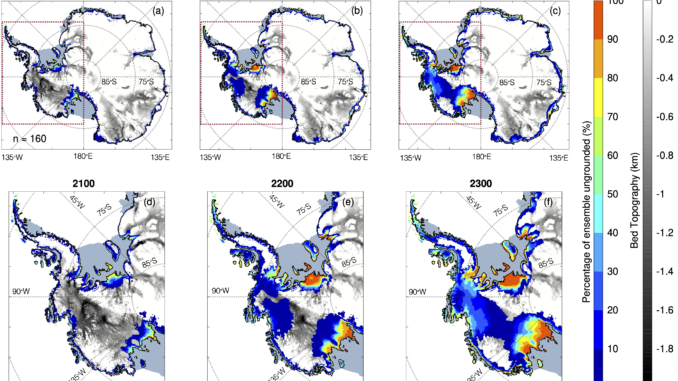
Numerical models simulating the evolution of the Antarctic Ice Sheet have mostly focused on the twenty-first century. How the ice sheet will evolve after 2100 remains highly uncertain, as several instability mechanisms could develop and destabilize vast regions of Antarctica. The article “Evolution of the Antarctic Ice Sheet Over the Next Three Centuries From an ISMIP6 Model Ensemble” investigates the behavior of the Antarctic Ice Sheet until 2300 using an ensemble of 16 different ice flow models.
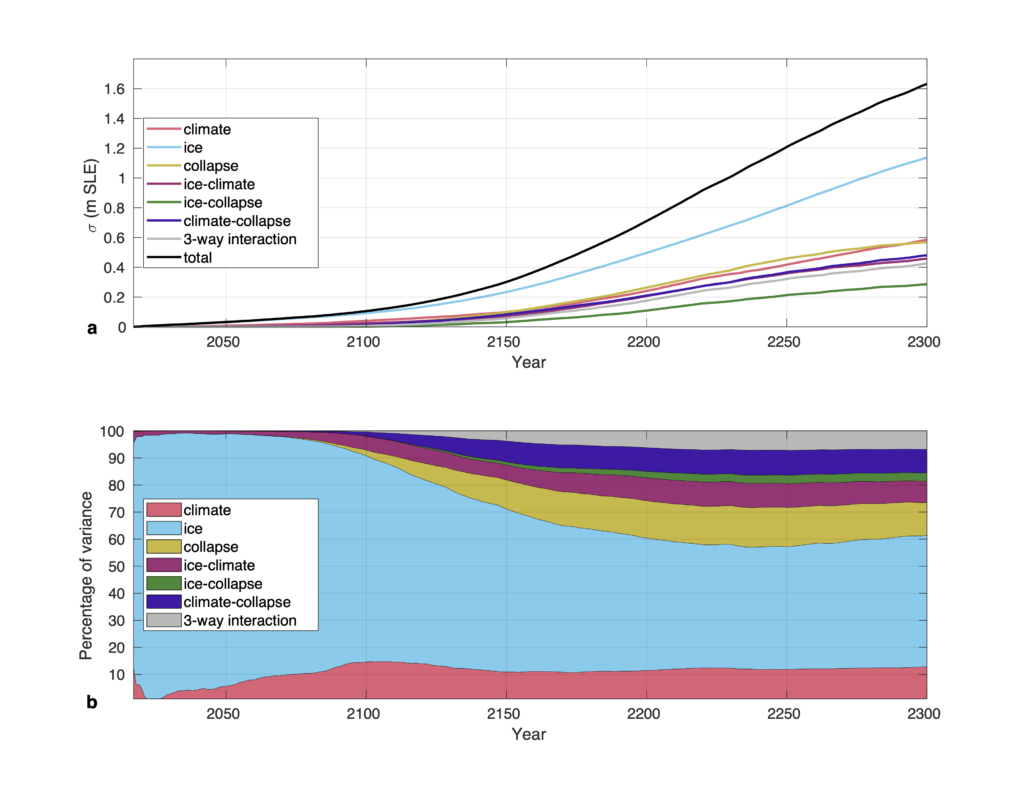
The results show that the Antarctic contribution to sea-level rise remains limited until 2100 but increases rapidly afterward. The ice retreats in most basins of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, and some numerical experiments suggest a near-complete collapse of this region by 2300. The time when these glaciers start retreating varies depending on the choice of ice flow model, but the speed at which they retreat is consistent among the models once the retreat begins. On a multi-century timescale, the choice of ice sheet model remains a leading source of uncertainties.
Reference: Seroussi, H., Pelle, T., Lipscomb, W. H., Abe-Ouchi, A., Albrecht, T., Alvarez-Solas, J., et al. Evolution of the Antarctic Ice Sheet over the next three centuries from an ISMIP6 model ensemble. Earth’s Future (2024). https://doi.org/10.1029/2024EF004561

Leave a Reply